No products in the cart.
Return To ShopWhy Low Frequency Works Best in Water Explained
Introduction
When people hear the word frequency, they often think of sound or radio waves in abstract terms. In aquatic environments, frequency choice is not theoretical. It directly determines whether a signal works or fails. This is one of the core reasons PIT tag technologies rely on low frequency systems, and it is also why military and naval operations depend heavily on low frequency signals underwater.
Frequency Basics Made Simple
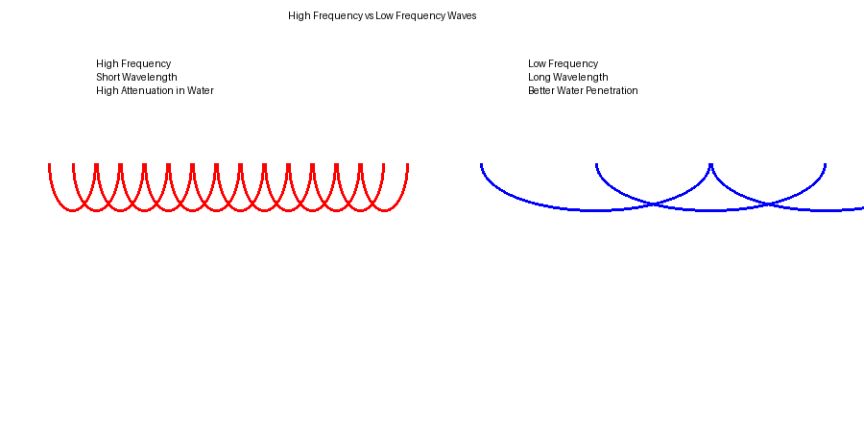
Frequency refers to how fast a wave oscillates. High frequency waves oscillate very quickly and have short wavelengths. Low frequency waves oscillate more slowly and have long wavelengths. These physical differences matter greatly once waves encounter water, tissue, sediment, or turbulence.
How Water Affects Frequency Performance
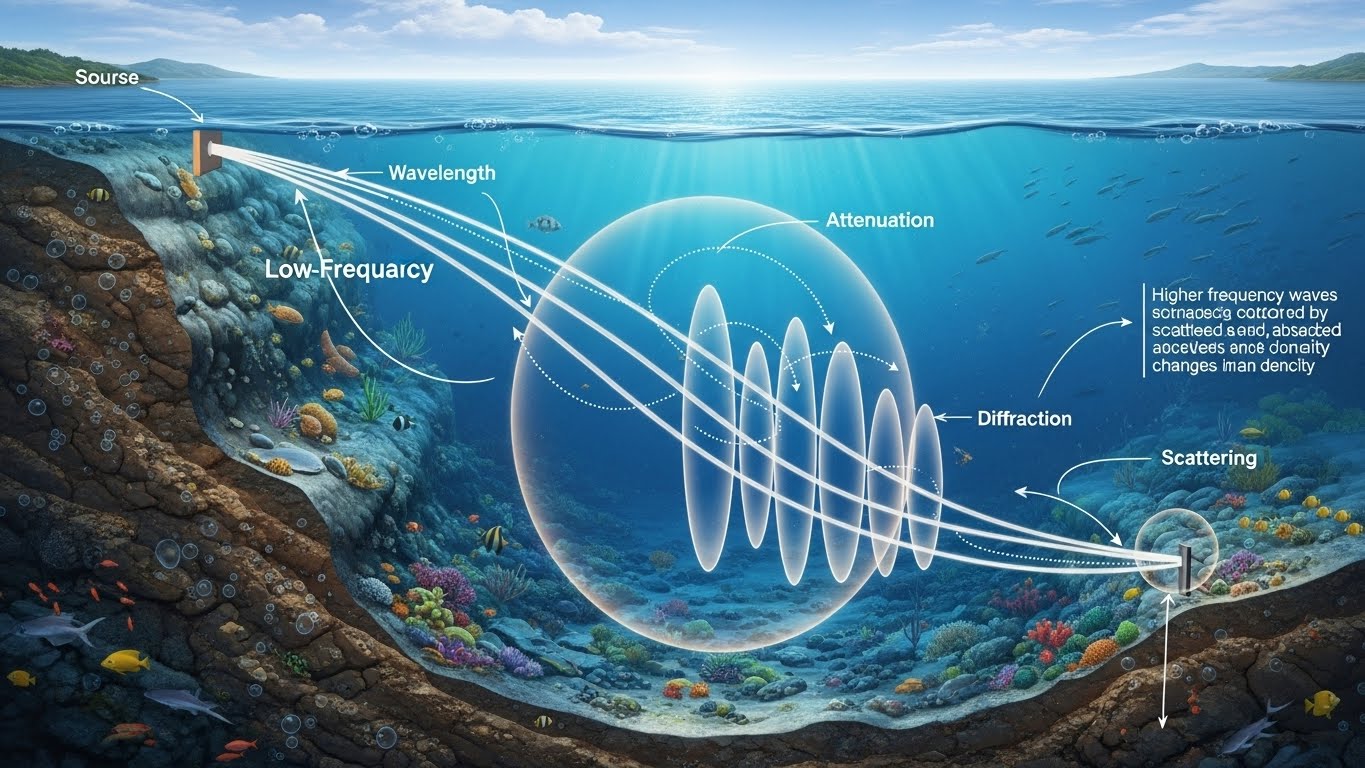
Water is a challenging medium for signal transmission because it absorbs energy, especially at higher frequencies. As frequency increases, attenuation increases.
High Frequency Waves
High frequency waves lose energy rapidly in water. They are easily absorbed or scattered, resulting in short detection ranges and inconsistent performance. This is why high frequency RFID systems work well in air but struggle in submerged environments.
Low Frequency Waves
Low frequency waves penetrate water, tissue, and sediment far more effectively. Their longer wavelengths allow them to pass through fish bodies, turbid water, and debris with minimal loss.
Why PIT Tags Use Low Frequency
PIT tags operate in the low frequency range because they offer reliable detection in freshwater and saltwater, consistent performance through fish tissue, minimal sensitivity to turbidity, and stable read ranges near antennas. This allows PIT tags to remain passive, long lasting, and dependable over years of monitoring.
The Same Frequency Strategy Used by the Military
Low frequency technology is not unique to fisheries science. Naval and military forces worldwide use low frequency systems for underwater communication and sonar. The reason is simple: low frequency signals travel farther in water with less loss. This same principle explains why low frequency PIT tags perform reliably underwater.
Why This Matters for Fisheries and Conservation
Choosing the correct frequency directly impacts data quality, fish welfare, and project success. Low frequency PIT tag systems allow researchers to detect tagged animals consistently, build long term datasets, and deploy arrays in challenging habitats.
Final Takeaway
High frequency systems excel in air and controlled environments. Low frequency systems excel in water and biological systems. That is why PIT tags rely on low frequency technology and why the same principles are trusted by military and naval operations worldwide.



Add comment